Clinical Information

High Digestibility
- Yeast Protein has a PDCAAS of 1.0 based on 5 lots of AA profile analysis and in vitro protein digestibility score of 84.91 ± 0.52%.4
- The PDCAAS of Yeast Protein is at the same level as WPC (whey protein concentrate), higher than SPI (soy protein isolate) for adults.4
-
- Yeast Protein increases the digestibility and absorption rate of proteins when used as a complimentary protein in blends.2
- Yeast Protein improves intestinal balance, increases microbial diversity, and promotes short chain fatty acids production.3
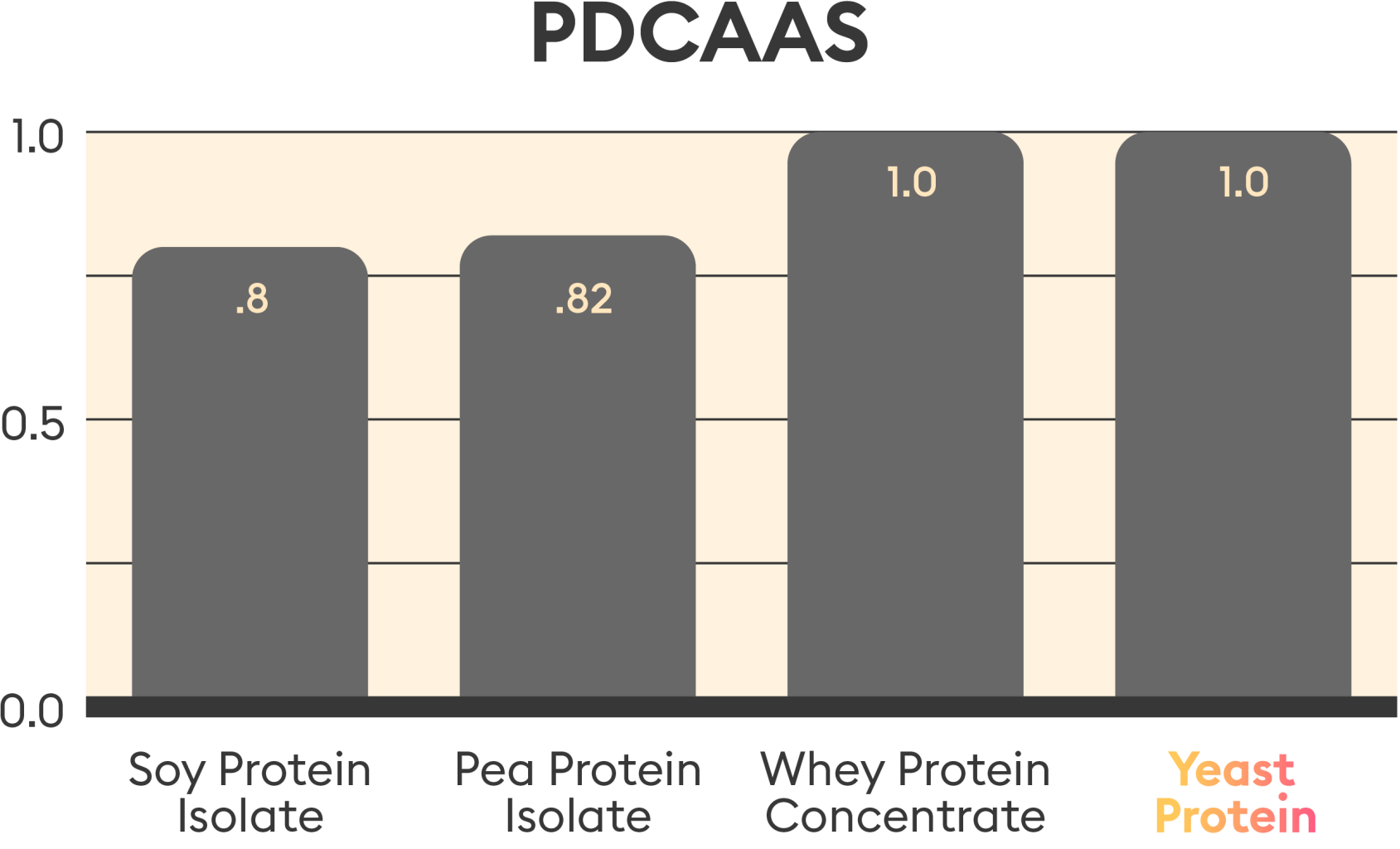
*Full report available upon request 4
Supports Muscle Recovery

- Yeast Protein is high in Branched Chain Amino Acids, which when broken down are converted into glucose, preventing muscle loss and promoting muscle recovery after exercise.1
- Experimental results showed that Yeast Protein contains ≥20.0% BCAA, higher than PPI and comparable to WPC.
- YESTEIN® is an excellent protein for sports nutrition and an aging population, to support muscular recovery and reduce muscular fatigue/loss.
- Yeast Protein increases lean muscle mass, strength, and endurance (when consumed twice per day at 20 grams per dose for 8 weeks) when combined with exercise in an aging population (40+ older).5
- Yeast Protein improves muscle morphology, muscle strength, increase muscle size and reverses muscle loss when combined with resistance training (Recommended Dosage: 1g/kg body weight per day for 3 months).3
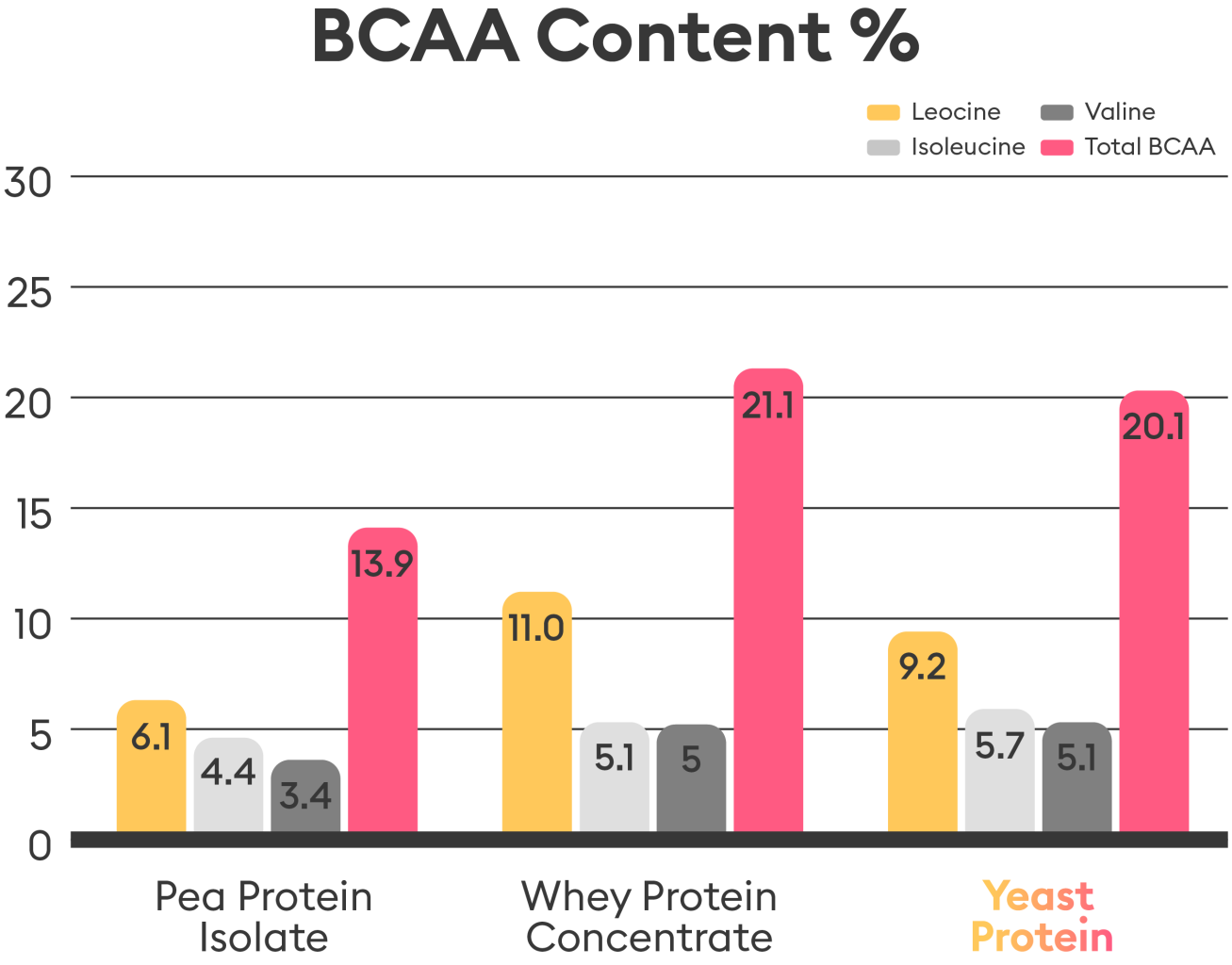
*Full report available upon request 2
Whey Equivalency
Methodology
- Participants: 116 healthy adult males aged 40+ were recruited, with 79 completing the study.
- Intervention: Participants were randomly assigned to consume 40g of either Yeast Protein, whey protein, or a placebo (maltodextrin) twice daily for 8 weeks.
- Exercise Regimen: Participants engaged in resistance training three times a week.
- Measurements: Body composition (via DEXA scans), muscle strength, and endurance were assessed at baseline, week 4, and week 8.
Results
- The Yeast Protein and whey protein groups increased lean trunk mass and total lean mass from baseline.5
- Yeast Protein is an effective and sustainable alternative to whey protein for improving lean mass, strength, and endurance in adults, particularly those with low protein intake.5
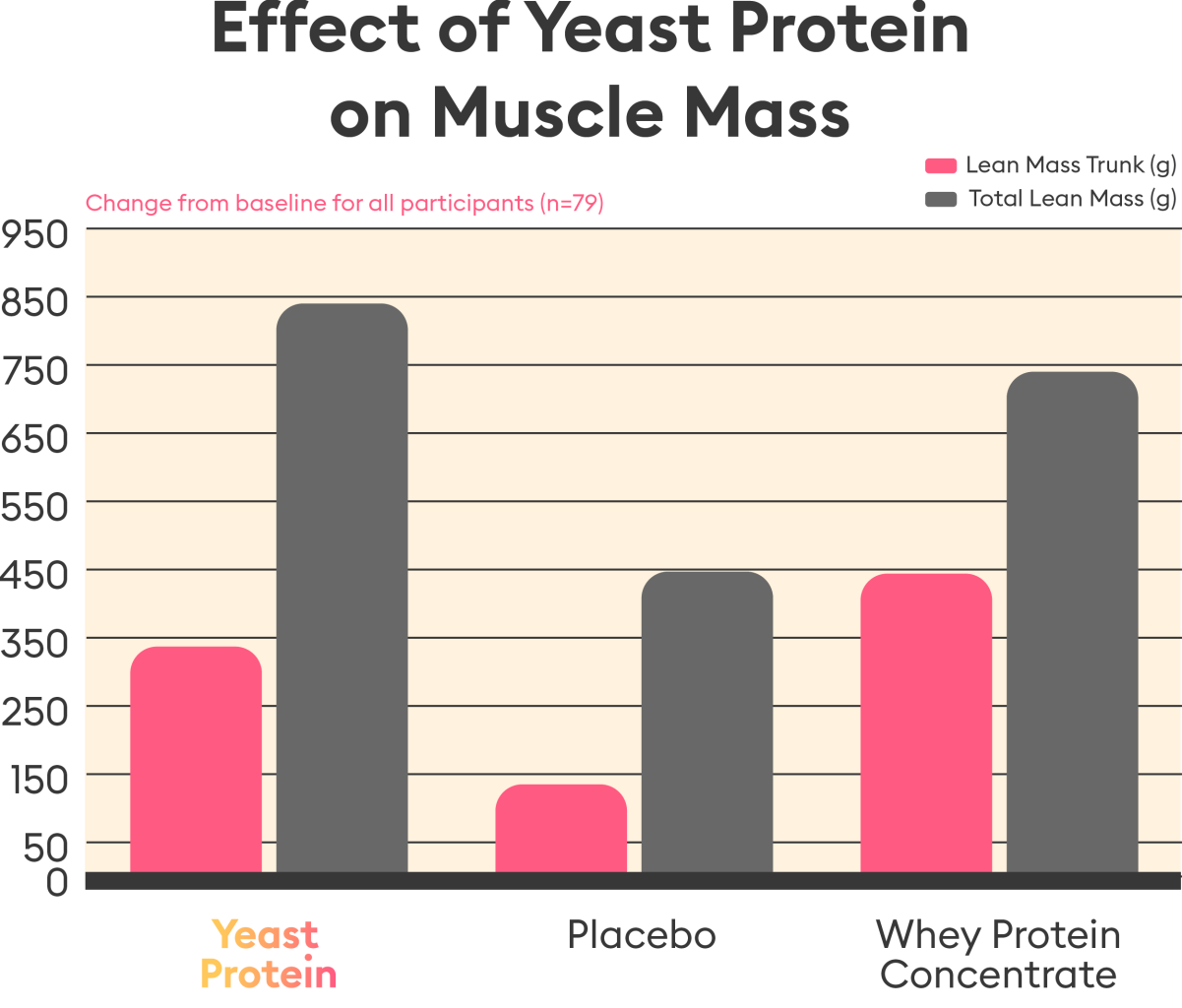
*Clinical Data available upon request 5
1 Xiaoqiao TANG; Yu WU; Jun FAN; Wenxiang YANG; Bolin FAN. Nutritional evaluation of yeast protein / 公共卫生与预防医学. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine; (6): 100-104, 2020
2 Chen Zhixian, Zhang Haibo, Zhang Shuangqing, Zhang Yan. Study on the amino acid composition and in vitro dynamic digestion of three kinds of proteins from differentsources. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition); Vol 40 (2); April 2019.
3 Yuxiao Liao et. al. Muscle aging amelioration by yeast protein supplementation was associated with gut microbiota. The Journal of Functional Foods. January 07, 2022:89: Elsevier 104948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2022.104948.
4 Chengxin Ma, Songgang Xia, Jian Song, Yukun Hou, Tingting Hao, Shuo Shen, Ku Li, Changhu Xue, Xiaoming Jiang, Yeast protein as a novel dietary protein source: Comparison with four common plant proteins in physicochemical properties, Current Research in Food Science, Volume 7, 2023.
5 D Briskey, RA Skinner, and A Rao, “Effect of Yeast Protein on Muscle Mass and Performance in an Adult Population – a Double Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial.” Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, vol. 12, no. 5 (2024): 292-300. doi: 10.12691/jfnr-12-5-9